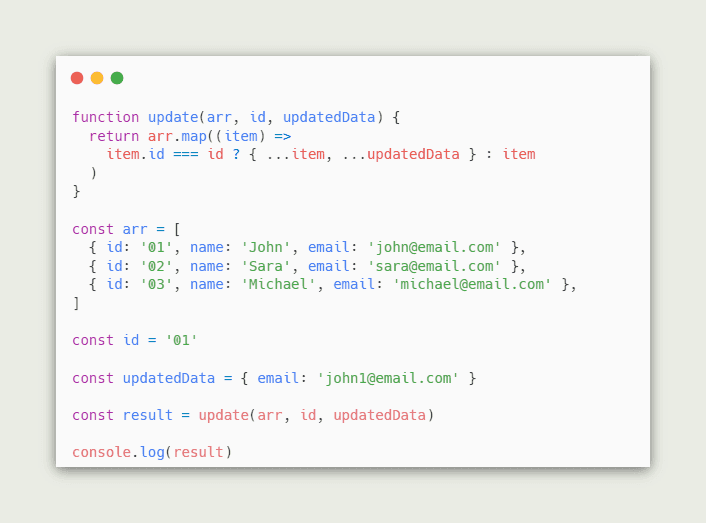
Update an Object’s Property in an Array of Objects using findIndex
To update an object’s property in an array of objects:
- Use the
findIndex()method to get the index of the object in the array. - Access the array at the index and update the object’s property.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
const index = arr.findIndex(obj => {
return obj.id === 2;
});
console.log(index); // 👉️ 1
arr[index].name = 'Alfred';
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
// { id: 2, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(arr);The Array.findIndex method returns the index of the first element in the array that satisfies the supplied testing function.
The function we passed to the Array.findIndex() method gets called with each element (object) in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over all array elements.
On each iteration, we check if the object has an id property with a value of 2 and return the result.
The last step is to use the index of the object to update the property in the array.
Note that the findIndex method returns -1 if no elements meet the condition.
If you need to handle this scenario, use an if statement.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
const index = arr.findIndex(obj => {
return obj.id === 123;
});
console.log(index); // 👉️ -1
if (index !== -1) {
arr[index].name = 'Alfred';
}
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
// { id: 2, name: 'Bob' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(arr);The if statement checks if the findIndex method found a matching object before updating its property.
Update an Object’s Property in an Array of Objects using map
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.map()method to iterate over the array. - Check if each object is the one to be updated.
- If the condition is met, update the property in the object.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 1, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
const newArr = arr.map(obj => {
if (obj.id === 1) {
return {...obj, name: 'Alfred'};
}
return obj;
});
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(newArr);The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element (object) in the array.
The map() method returns a new array containing the values returned from the callback function.
Using the map() method is useful when you need to update the properties of multiple objects in the array.
The map() method doesn’t mutate the original array, it returns a new array.
On each iteration, we check if the object has an id property equal to 1.
If the condition is met, we use the spread syntax (…) to unpack the other key-value pairs of the object and override the name property.
If the condition is not met, we return the object as is.
Notice that our array has 2 objects with an id of 1.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 1, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
const newArr = arr.map(obj => {
if (obj.id === 1) {
return {...obj, name: 'Alfred'};
}
return obj;
});
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(newArr);Update an Object’s Property in an Array of Objects using for...of
You can also use the for...of loop to update an object’s property in an array of objects.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 1, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
for (const obj of arr) {
if (obj.id === 1) {
obj.name = 'Alfred';
break;
}
}
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 1, name: 'Bob' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(arr);The for…of statement is used to loop over iterable objects like arrays, strings, Map, Set and NodeList objects and generators.
On each iteration, we check if the id property of the object is equal to 1.
If the condition is met, we update the value of the name property and use the break statement to exit the for loop.
We only want to update the first object that matches the condition, so we short-circuit to avoid unnecessary work.
If you need to update all objects that match the condition, remove the break statement.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 1, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
for (const obj of arr) {
if (obj.id === 1) {
obj.name = 'Alfred';
}
}
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 1, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(arr);There are 2 objects with an id of 1 in the array, so the name property in both objects got updated.
Alternatively, you can use the Array.find() method.
Update an Object’s Property in an Array of Objects using find
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
find()method to find the object in the array. - Update the properties on the object.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
const obj = arr.find(obj => {
return obj.id === 2;
});
console.log(obj); // 👉️ { id: 2, name: 'Bob' }
if (obj !== undefined) {
obj.name = 'Alfred';
}
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
// { id: 2, name: 'Alfred' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
// ]
console.log(arr);The Array.find method returns the first element in the array that satisfies the provided testing function.
In the example, the find() method returns the first object in the array that has an id property with a value of 2.
The find() method returns undefined if no element matches the condition, so we used an if statement to make sure a matching object is found.
The found object and the object that’s stored in the array have the same reference, so we can update the object directly and the changes will be reflected in the array.
Update an Object’s Property in an Array of Objects using for
You can also use a basic for loop to update an object’s property in an array.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
if (arr[index].id === 2) {
arr[index].name = 'Alfred';
break;
}
}
[
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Alfred'},
{id: 3, name: 'Charlie'},
];
console.log(arr);The syntax for a basic for loop is a bit more verbose and requires us to make use of the index to access the current object.
On each iteration, we check if the current object has an id with a value of 2 and update the matching object.
We also used the break statement to exit the loop once the matching object is updated.
Change a Value of an Object in an Array using Array.slice()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.findIndex()method to get the index of the object in the array. - Use the
Array.slice()method to get the slices of the array before and after the object. - Combine the two slices with the updated object.
const arr = [
{id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
{id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
{id: 3, name: 'Carl'},
];
const index = arr.findIndex(object => {
return object.id === 2;
}); // 👉️ 1
let updatedArray = [];
if (index !== -1) {
const updatedObject = {...arr[index], name: 'John'};
updatedArray = [
...arr.slice(0, index),
updatedObject,
...arr.slice(index + 1),
];
}
// [
// { id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
// { id: 2, name: 'John' },
// { id: 3, name: 'Carl' }
// ]
console.log(updatedArray);We used the Array.findIndex() method to get the index of the object in the array.
Our if statement makes sure the object with the specified value exists.
We used the spread syntax (…) to change the value of the name property of the object and used the Array.slice() method to slice the array.
We passed the following arguments to the Array.slice method:
- start index – the index at which to start extracting items.
- end index – extract items up to, but not including this index.
The first call to the Array.slice() method selects the objects up to, but not including the object to be updated.
if (index !== -1) {
const updatedObject = {...arr[index], name: 'John'};
updatedArray = [
...arr.slice(0, index),
updatedObject,
...arr.slice(index + 1),
];
}We then place the updated object in the array.
The second call to the Array.slice() method starts at the index after the index of the object to be updated.
This approach doesn’t mutate the original array of objects, we simply create a new array with the updated object.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I’d use the Array.map() method to avoid mutating the original array as I find it the most intuitive.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference.
I’d use the Array.findIndex() method to update a single object in the array and the Array.map() method if I need to update all objects that match the condition.



 Filter an array of objects based on a property – JavaScript
Filter an array of objects based on a property – JavaScript