UPDATE Statment
UPDATE statement is a SQL DML statement used to change and update the data in tables. We will explain the UPDATE statement with sample applications. Let’s take a look at how this expression is used.
UPDATE table_name SET = column1 = new_value, column2 = new_value WHERE conditionNow let’s write our codes, for this, let’s see our table first.
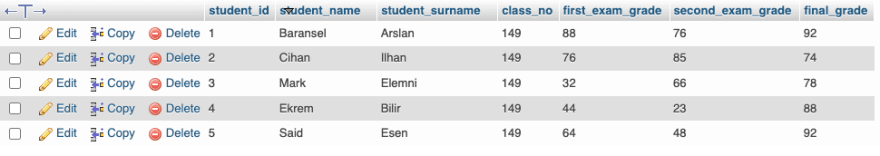
For example, let’s add 10 points to the second exam grade of the student whose name is Baransel;
UPDATE students SET second_exam_grade = second_exam_grade + 10 WHERE student_name = 'Baransel'Now let’s look at our table:
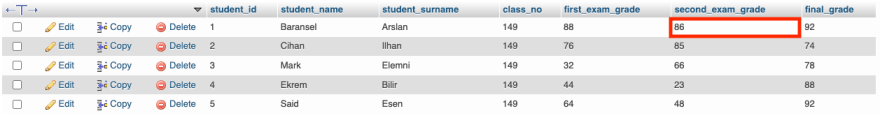
Let’s do another example, this time, let’s add 10 points to both the first exam grade and the final grade of all students whose first exam grade is less than 50.
UPDATE students SET first_exam_grade = first_exam_grade + 10, final_grade = final_grade + 10 WHERE first_exam_grade < 50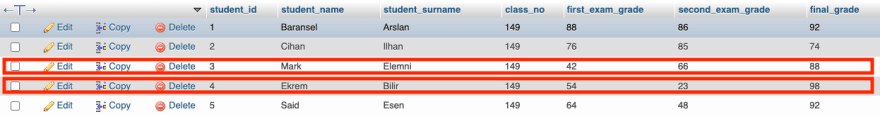
Mark’s and Ekrem’s first exam grades is less than 50, 10 points were added to first exam grade and final grade.
DELETE Statment
The DELETE statement is the SQL Data Manipulation Language statement used to delete data in a table. With the DELETE statement, the entire data in the table or the data that meets a certain condition is deleted.
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE conditionFor example, let’s delete students whose surnames does not start with the letter “E” from the table;
DELETE FROM students WHERE student_surname NOT LIKE 'E%'Thus, we deleted 3 students from the table. Let’s take a look at the final version of our table.

DELETE FROM studentsAs you can see we have deleted all the data inside our table. The point to note here is that we can delete the data in the table with the DELETE statement, but not the tables. If you want to delete the table, not the data in the table, you can refer to the DROP statement in the SQL DDL Commands.



 7 Alternatives to the div Tag in HTML
7 Alternatives to the div Tag in HTML