To follow this article you need to understand the following topics:
Analogy

uppose you have a bunch of songs on your computer.
For each artist, you have a number of plays.
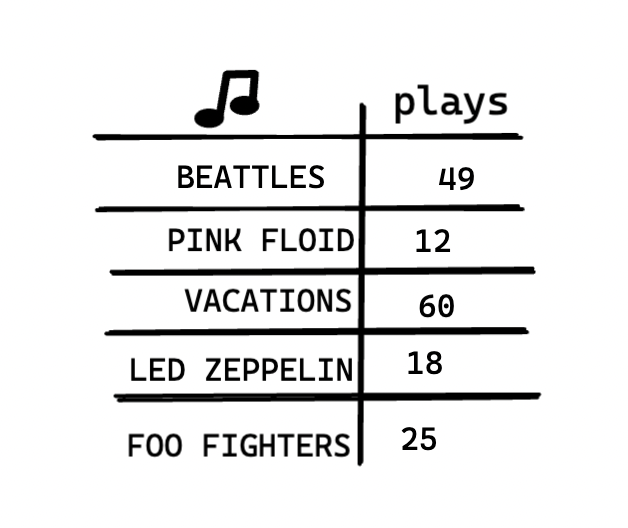
You want to sort this list from most to least played, so that you can rank your favourite artists. How can you do it?
One way is go through the list and find the most played artist. Add that artist to a new list.
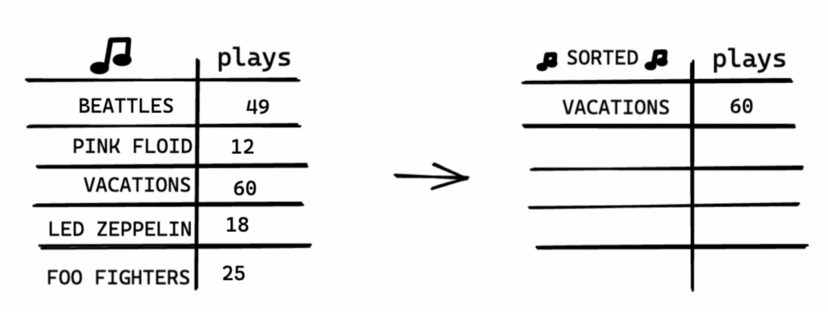
Do it again to find the next most played artist.
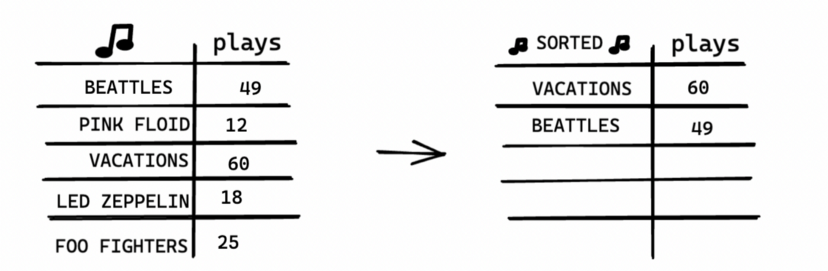
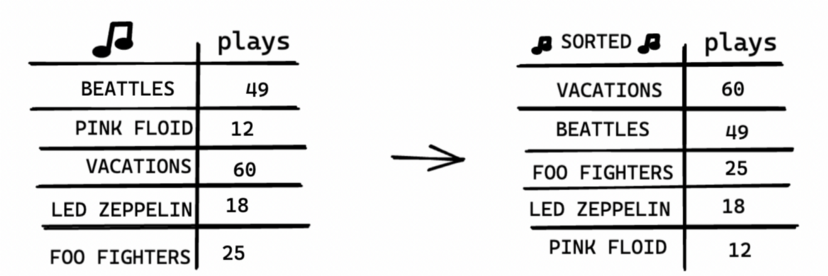
Keep doing this, and you’ll end up with a sorted list.
Time complexity
To find the artist with the highest number of plays, you have to check each item in the list. This takes O(n) time, as you just saw. So you have an operation that takes O(n) time and you have to do that n times:
This tikes O(n x n) time or O(n^2) time.
Example code listing
Sort an array from smallest to largest.
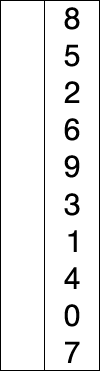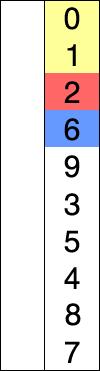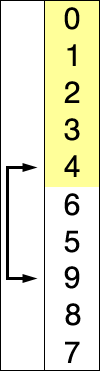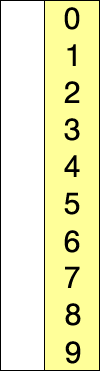
Let’s write a function to find the smallest element in an array:
// Search the remainder of the array for the smallest number
function findSmallest(nums, index) {
let smallest = nums[index];
let swapIndex = index;
for (let i = index + 1; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < smallest) {
smallest = nums[i];
swapIndex = i;
}
}
return { swapIndex, smallest };
}Now you can use this function to write the selection sort:
const selectionSort = (nums) => {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
const { smallest, swapIndex } = findSmallest(nums, i);
// Swap if the smallest number isn't at the current index
if (i !== swapIndex) {
const tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = smallest;
nums[swapIndex] = tmp;
}
}
return nums;
};Summary
- Selection sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted part and putting it at the beginning.
Resources
- Wikipedia
- Geeks for geeks
- Grokking algorithms (book)


 How to Check If a Value Exists in an Object Using JavaScript?
How to Check If a Value Exists in an Object Using JavaScript?